Areas
To visualize data correctly, the dashboard needs to know your administrative boundaries. The Areas interface provides a comprehensive directory for managing every individual geographic unit across all levels of the defined hierarchy. This is where names, codes, and map availability are displayed.
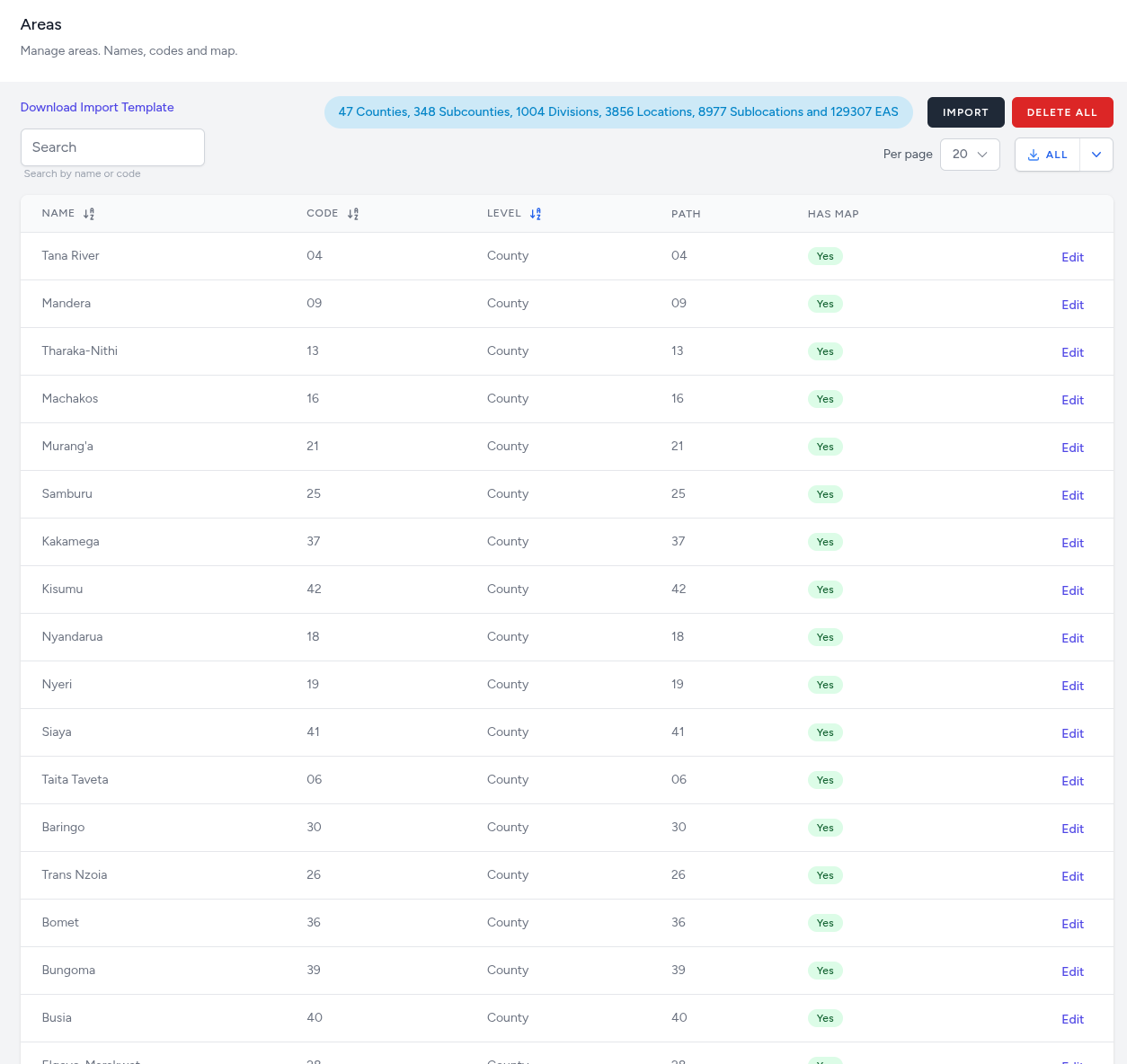
Areas Administrative View
The primary dashboard for Areas provides a searchable, sortable list of every geographic entity in the system.
Search and Discovery: A real-time Search bar allows administrators to locate specific areas by name or code.
- Download Import Template: Provides a standardized file format for bulk-uploading geographic data.
- Import: Allows for the rapid population of the area database via file upload.
- Delete All: A protected action to wipe the current area list for full re-indexing.
Summary Statistics: A status badge at the top displays a real-time count of total entities per level (e.g., 47 Counties, 348 Subcounties... 129307 EAs).
Importing Areas
The Import interface allows administrators to upload hierarchical data containing area maps, names, and codes. Users can toggle between two specialized upload methods depending on the data source.
Shapefile Import
The Shapefile tab is used to import spatial data and map boundaries for specific levels of the hierarchy.
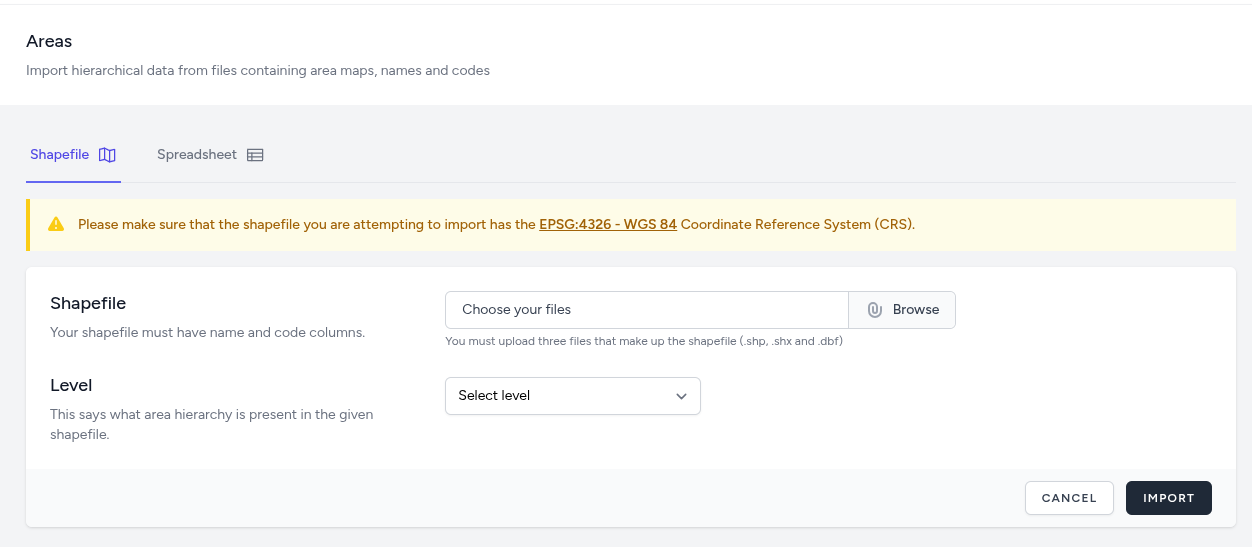
-
Coordinate System Requirement: All uploaded shapefiles must use the EPSG:4326 - WGS 84 Coordinate Reference System (CRS) to ensure compatibility with the dashboard's map engine.
-
File Requirements: Users must upload the three core files that constitute a valid shapefile: .shp, .shx, and .dbf.
-
Data Structure: The shapefile's attribute table must contain dedicated columns for area names and unique codes.
-
Level Selection: Administrators must select which specific Area Hierarchy level (e.g., County, EA) is represented in the provided shapefile.
Spreadsheet Import
The Spreadsheet tab is used to import the complete administrative hierarchy from a single flat file.
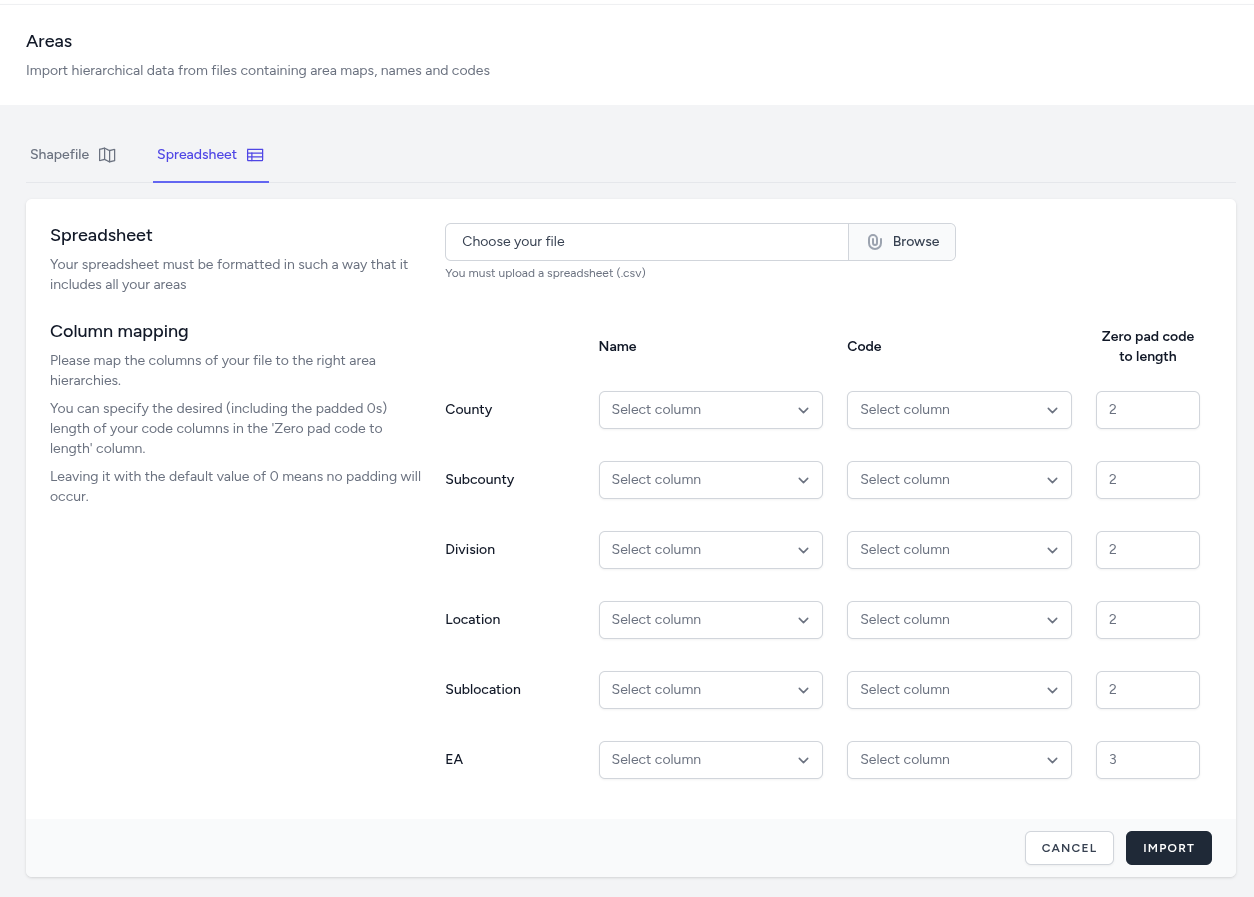
-
File Format: The system accepts .csv files formatted to include all areas across the hierarchical structure.
-
Column Mapping: For every level in the hierarchy (from the first to the last), the user must map the corresponding columns from their file to the appropriate fields:
-
Name: The column containing the display name for that level.
-
Code: The column containing the unique identifier for that level.
-
On-the-Fly Zero Padding: The interface allows users to specify the Zero pad code to length for each level during the import process.
-
Note: The default value of 0 means no padding will occur.